What has Perseverance found in two years on Mars?
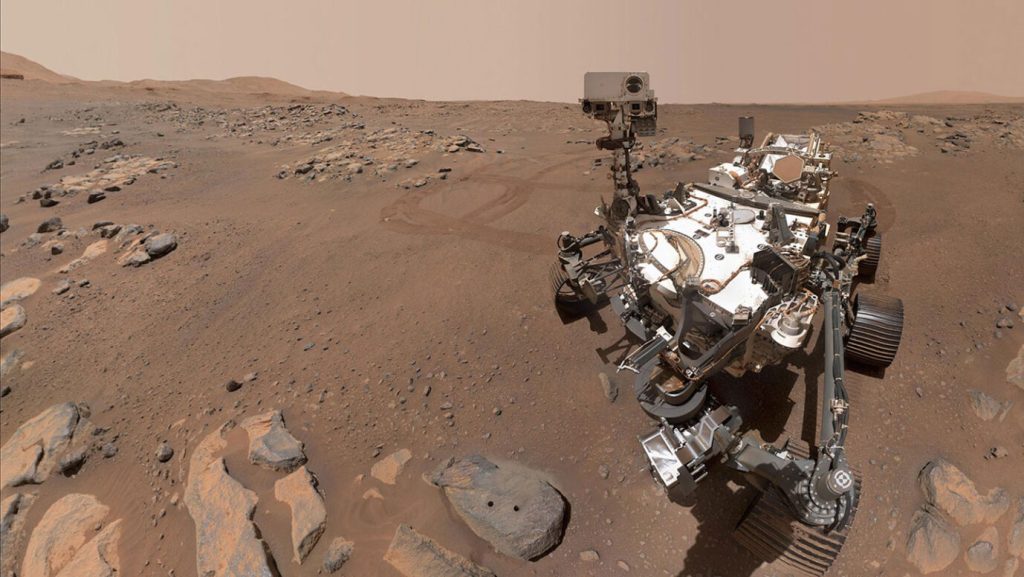

In August 2021 on a lonely crater floor, the newest Mars rover dug into one of its first rocks.
The percussive drill attached to the arm of the Perseverance rover scraped the dust and top several millimeters off a rocky outcrop in a 5-centimeter-wide circle. From just above, one of the rover’s cameras captured what looked like broken shards wedged against one another. The presence of interlocking crystal textures became obvious. Those textures were not what most of the scientists who had spent years preparing for the mission expected.
Then the scientists watched on a video conference as the rover’s two spectrometers revealed the chemistry of those meshed textures. The visible shapes along with the chemical compositions showed that this rock, dubbed Rochette, was volcanic in origin. It was not made up of the layers of clay and silt that would be found at a former lake bed.
Nicknamed Percy, the rover arrived at the Jezero crater two years ago, on February 18, 2021, with its sidekick helicopter, Ingenuity. The most complex spacecraft to explore the Martian surface, Percy builds on the work of the Curiosity rover, which has been on Mars since 2012, the twin Spirit and Opportunity rovers, the Sojourner rover and other landers.
But Perseverance’s main purpose is different. While the earlier rovers focused on Martian geology and understanding the planet’s environment, Percy is looking for signs of past life. Jezero was picked for the Mars 2020 mission because it appears from orbit to be a former lake environment where microbes could have thrived, and its large delta would likely preserve any signs of them. Drilling, scraping and collecting pieces of the Red Planet, the rover is using its seven science instruments to analyze the bits for any hint of ancient life. It’s also collecting samples to return to Earth.
Since landing, “we’ve been able to start putting together the story of what has happened in Jezero, and it’s pretty complex,” says Briony Horgan, a planetary scientist at Purdue University in West Lafayette, Ind., who helps plan Percy’s day-to-day and long-term operations.
Volcanic rock is just one of the surprises the rover has uncovered. Hundreds of researchers scouring the data Perseverance has sent back so far now have some clues to how the crater has evolved over time. This basin has witnessed flowing lava, at least one lake that lasted perhaps tens of thousands of years, running rivers that created a mud-and-sand delta and heavy flooding that brought rocks from faraway locales.
Jezero has a more dynamic past than scientists had anticipated. That volatility has slowed the search for sedimentary rocks, but it has also pointed to new alcoves where ancient life could have taken hold.
Perseverance has turned up carbon-bearing materials — the basis of life on Earth — in every sample it has abraded, Horgan says. “We’re seeing that everywhere.” And the rover still has much more to explore.
Perseverance finds unexpected rocks
Jezero is a shallow impact crater about 45 kilometers in diameter just north of the planet’s equator. The crater formed sometime between 3.7 billion and 4.1 billion years ago, in the solar system’s first billion years. It sits in an older and much larger impact basin known as Isidis. At Jezero’s western curve, an etched ancient riverbed gives way to a dried-out, fan-shaped delta on the crater floor.
That delta “is like this flashing signpost beautifully visible from orbit that tells us there was a standing body of water here,” says astrobiologist Ken Williford of Blue Marble Space Institute of Science in Seattle.
Perseverance landed on the crater floor about two kilometers from the front of the delta. Scientists thought they’d find compacted layers of soil and sand there, at the base of what they dubbed Lake Jezero. But the landscape immediately looked different than expected, says planetary geologist Kathryn Stack Morgan of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif. Stack Morgan is deputy project scientist for Perseverance.
For the first several months after the landing, the Mars 2020 mission team tested the rover’s movements and instruments, slowly, carefully. But from the first real science drilling near the landing location, researchers back on Earth realized what they had found. The texture of the rock, Stack Morgan says, was “a textbook igneous volcanic rock texture.” It looked like volcanic lava flows.
Over the next six months, several more rocks on the crater floor revealed igneous texture. Some of the most exciting rocks, including Rochette, showed olivine crystals throughout. “The crystal fabric was obviously cooled from a melt, not transported grains,” as would be the case if it were a sedimentary sample, says Abigail Allwood of the Jet Propulsion Lab. She leads the rover’s PIXL instrument, which uses an X-ray beam to identify each sample’s composition.
Mission scientists now think the crater floor is filled with igneous rocks from two separate events — both after the crater was created, so more recently than the 3.7 billion to 4.1 billion years ago time frame. In one, magma from deep within the planet pushed toward the surface, cooled and solidified, and was later exposed by erosion. In the other, smaller lava flows streamed at the surface.
Sometime after these events, water flowed from the nearby highlands into the crater to form a lake tens of meters deep and lasting tens of thousands of years at least, according to some team members. Percy’s instruments have revealed the ways that water altered the igneous rocks: For example, scientists have found sulfates and other minerals that require water to form, and they’ve seen empty pits within the rocks’ cracks, where water would have washed away material. As that water flowed down the rivers into the lake, it deposited silt and mud, forming the delta. Flooding delivered 1.5-meter-wide boulders from that distant terrain. All of these events preceded the drying of the lake, which might have happened about 3 billion years ago.
Core samples, which Perseverance is collecting and storing on board for eventual return to Earth, could provide dates for when the igneous rocks formed, as well as when the Martian surface became parched. During the time between, Lake Jezero and other wet environments may have been stable enough for microbial life to start and survive.
“Nailing down the geologic time scale is of critical importance for us understanding Mars as a habitable world,” Stack Morgan says. “And we can’t do that without samples to date.”
About a year after landing on Mars, Perseverance rolled several kilometers across the crater floor to the delta front — where it encountered a very different geology.
The delta might hold signs of ancient life
Deltas mark standing, lasting bodies of water — stable locales that could support life. Plus, as a delta grows over time, it traps and preserves organic matter.
Sand and silt deposited where a river hits a lake get layered into sedimentary material, building up a fan-shaped delta. “If you have any biological material that is trapped between that sediment, it gets buried very quickly,” says Mars geologist Eva Scheller of MIT, a researcher with the Percy team. “It creates this environment that is very, very good for preserving the organic matter.”
While exploring the delta front between April 2022 and December 2022, Perseverance found some of the sedimentary rocks it was after.
Several of the rover’s instruments zoomed in on the textures and shapes of the rocks, while other instruments collected detailed spectral information, revealing the elements present in those rocks. By combining the data, researchers can piece together what the rocks are made of and what processes might have changed them over the eons. It’s this chemistry that could reveal signs of ancient Martian life — biosignatures. Scientists are still in the early stages of these analyses.
There won’t be one clear-cut sign of life, Allwood says. Instead, the rover would more likely reveal “an assemblage of characteristics,” with evidence slowly building that life once existed there.
Chemical characteristics suggestive of life are most likely to hide in sedimentary rocks, like those Perseverance has studied at the delta front. Especially interesting are rocks with extremely fine-grained mud. Such mud sediments, Horgan says, are where — in deltas on Earth, at least — organic matter is concentrated. So far, though, the rover hasn’t found those muddy materials.
But the sedimentary rocks studied have revealed carbonates, sulfates and unexpected salts — all materials indicating interaction with water and important for life as we know it. Percy has found carbon-based matter in every rock it has abraded, Horgan says.
“We’ve had some really interesting results that we’re pretty excited to share with the community,” Horgan says about the exploration of the delta front. Some of those details may be revealed in March at the Lunar and Planetary Science Conference.
Perseverance leaves samples for a future mission
As of early February, Perseverance has collected 18 samples, including bits of Mars debris and cores from rocks, and stored them on board in sealed capsules for eventual return to Earth. The samples come from the crater floor, delta front rocks and even the thin Martian atmosphere.
In the final weeks of 2022 and the first weeks of 2023, the rover dropped — or rather, carefully set down — half of the collected samples, as well as a tube that would reveal whether samples contained any earthly contaminants. These captured pieces of Mars are now sitting at the front of the delta, at a predetermined spot called the Three Forks region.
If Perseverance isn’t functioning well enough to hand over its onboard samples when a future sample-return spacecraft arrives, that mission will collect these samples from the drop site to bring back to Earth.
Researchers are currently working on designs for a joint Mars mission between NASA and the European Space Agency that could retrieve the samples. Launching in the late 2020s, it would land near the Perseverance rover. Percy would transfer the samples to a small rocket to be launched from Mars and returned to Earth in the 2030s. Lab tests could then confirm what Perseverance is already uncovering and discover much more.
Meanwhile, Percy is climbing up the delta to explore its top, where muddy sedimentary rocks may still be found. The next target is the edge of the once-lake, where shallow water long ago stood. This is the site Williford is most excited about. Much of what we know about the history of how life has evolved on Earth comes from environments with shallow water, he says. “That’s where really rich, underwater ecosystems start to form,” he says. “There’s so much going on there chemically.”